
CHAPPIDI ABHIRATH REDDY
C/O COL GKS REDDY
Secunderabad - 500015
Syria Currency
Syria Currency
The Syrian pound (sign: LS or £S; Arabic: الليرة السورية al-līra as-sūriyya, French: livre syrienne; ISO code: SYP) is the currency ofSyria and is issued by the Central Bank of Syria. The pound is subdivided into 100 qirsh (Arabic: قرش plural: قروش, qorush, piastres inEnglish or French), although coins in qirsh are no longer issued.
Before 1947, the word qirsh was spelled with the initial Arabic letter غ, after which the word began with ق. Until 1958, banknotes were issued with Arabic on the obverse and French on the reverse. After 1958, English has been used on the reverses, hence the three different names for this currency. Coins used both Arabic and French until Syrian independence, then only Arabic.
The standard abbreviation for the Syrian pound is SYP. On 5 December 2005, the selling rate quoted by the Commercial Bank of Syria was 58.4 SYP to the US dollar. A rate of about 50 pounds to one dollar has been usual in the early 2000s, but the exchange rate is subject to fluctuations. Since the start of the Syrian civil war against the president Bashar Al Assad in 2011, the exchange rate of the Syrian pound has deteriorated quickly from 47 SYP for US$1 in March 2011 to over 200 SYP for US$1 in June 2013. Hard currencies such as the USD, CAD, GBP or Euro cannot be bought from banks or exchange companies; the black market is the only source of foreign currencies available to Syrian businessmen, students and those who want to travel abroad. The maximum amount that is allowed to be taken out with the Syrian traveler is US$3,000 per flight per year. Any amount in excess of US$3,000 is confiscated by the authorities and the Syrian traveler will risk spending a long time in what is called "economic affairs court". The Syrian pound is not a hard currency, and there are restrictions on its export (the maximum amount is 2,500 SYP per person).
History
During the period when Syria was a part of Ottoman Empire - which lasted about 400 years - the Ottoman lira was the currency. Following the fall of the Ottoman Empire and the placing of Syria under a mandate (French Occupation), the Egyptian pound was used in the territories under French and British mandates, including Lebanon, Transjordan andPalestine. Upon taking Lebanon and Syria under its separate mandate, the French government sought to replace the Egyptian currency and granted a commercial bank, the Banque de Syrie (a French affiliate of the Ottoman Bank), the authority to issue a currency for states under its new mandate.
The pound (or livre as it was then known) was introduced in 1919 and was pegged at a value of 20 French francs[citation needed]. As the political status of Lebanon evolved, the Banque de Syrie, which was to act as the official bank for Lebanon and Syria, was renamed the Banque de Syrie et du Grand-Liban (BSL). The BSL issued the Lebanese-Syrian currency for 15 years, starting in 1924. Two years before the expiration of the 15-year period, the BSL split the Lebanese-Syrian currency into two separate currencies that could still be used interchangeably in either state. In 1939, the bank was renamed the Banque de Syrie et du Liban.
In 1941, the peg to the French franc was replaced by a peg to the British pound of 8.83125 Syrian pounds = 1 British pound, as a consequence of the occupation of Syria by British and Free French forces. This rate was based on the pre-war conversion rate between the franc and sterling. In 1946, following devaluation of the franc, the Syrian pound was pegged once again to the franc at a rate of 1 pound = 54.35 francs. In 1947, the U.S. dollar was adopted as the peg for the Syrian currency, with 2.19148 pounds = 1 dollar, a rate which was maintained until 1961. The Lebanese and Syrian currencies split in 1948. From 1961, a series of official exchange rates were in operation, alongside a parallel, black market rate which reflected the true market rate for Syrian pounds in Jordan and Lebanon where there was a healthy trade in the Syrian currency. The market was allowed to flourish because everybody, including government and public sector companies, needed it. The black market rate diverged dramatically from the official rate in the 1980s.
My Collection of Syrian Coins
25 Piastres – Syria - Nickel - 1979
Fifty Piastres – Syria - Nickel - 1979
One Pound – Syria - FAO – Nickel - 1968
One Pound – Syria - Nickel - 1979
One Pound – Syria - Small - Nickel - 1991
Two Pounds – Syria - Ancient Ruins - 1996
Five Pounds – Syria - Old Fort - 2003
Ten Pounds - Syria - Ancient Ruins - 2003
Turkey Currency
The Turkish lira (Currency sign: ₺ / 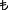 ; Turkish: Türk lirası) is the currency of Turkey and the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus(recognised only by Turkey). The Turkish lira is subdivided into 100 kuruş.
; Turkish: Türk lirası) is the currency of Turkey and the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus(recognised only by Turkey). The Turkish lira is subdivided into 100 kuruş.
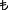 ; Turkish: Türk lirası) is the currency of Turkey and the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus(recognised only by Turkey). The Turkish lira is subdivided into 100 kuruş.
; Turkish: Türk lirası) is the currency of Turkey and the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus(recognised only by Turkey). The Turkish lira is subdivided into 100 kuruş.
History
Ottoman Lira (1844 - 1923)
After the last vestige of the ancient Roman Empire collapsed with the Fall of Constantinople to the Ottomans, today's Turkish State Mint was founded by Mehmed II. The first golden coin was minted in the name of "The Conqueror" in 1467.
The Ottoman lira was introduced as the main unit of currency in 1844, with the former currency, kuruş, remaining as a 1/100 subdivision. The Ottoman lira remained in circulation until the end of 1927.
First Turkish Lira (1923 - 2005)
Historical banknotes from the second, third and fourth issues have portraits of İsmet İnönü on the obverse side. This change was done according to the 12 January 1926 issue of the official gazette and canceled by the Democrat Party after World War II.
Second Turkish Lira (2005 - Till Date)
In December 2003, the Grand National Assembly of Turkey passed a law that allowed for redenomination by the removal of six zeros from the Turkish lira, and the creation of a new currency. It was introduced on 1 January 2005, replacing the previous Turkish lira (which remained valid in circulation until the end of 2005) at a rate of 1 second Turkish lira (ISO 4217 code "TRY") = 1,000,000 first Turkish lira (ISO 4217 code "TRL"). With the revaluation of the Turkish lira, the Romanian leu (also revalued in July 2005) briefly became the world's least-valued currency unit. At the same time, the Government introduced two new banknotes called TRY100 and TRY50. One EU diplomat has stated that Turkey will adopt the Euro if it joins the European Union.
In the transition period between January 2005 and December 2008, the second Turkish lira was officially called Yeni Türk Lirası (New Turkish lira). It was officially abbreviated "YTL" and subdivided into 100 new kuruş (yeni kuruş). Starting in January 2009, the "new" marking was removed from the second Turkish lira, its official name becoming just "Turkish lira" again, abbreviated "TL".
All obverse sides of current banknotes and reverse sides of current coins have portraits of Mustafa Kemal Atatürk.
My Collection of Turkish Coins
One Kurush – Turkey - Nickel - AH 1293 AD 1876
Ten Para – Turkey - Copper - AH 1293, AD 1876
Ten Kurus – Turkey - Nickel - 1956
Ten Bin Lira – Turkey - Nickel - 1995
1000 Lira – Turkey - Nickel - 1990
Jordan Currency.
The dinar (Arabic: دينار, ISO 4217 code JOD; unofficially known as JD) is the currency of Jordan. The dinar is divided into 10 dirham, 100 qirsh (also called piastres) or 1000 fulus.
The Jordanian dinar continued to be used in the West Bank along with Israeli currency after Israel took control of it in 1967. During Israel's hyperinflation in the 1970s and 1980s, the Jordanian currency provided stability.
History
From 1927 to 1950, the Palestine Currency Board issued Palestine pound as the official currency in both Palestine and the Trans-Jordan Emirate. After Jordan became an independent kingdom on 25 May 1946, the idea of issuing a national currency arose and led to the passing of the Provisional Act No. 35 of 1949. Under this Act, the Jordan Currency Board was formed, which became the sole authority entitled to issue Jordanian currency in the kingdom. The London-based entity consisted of a president and four members. As of 1 July 1950, the Jordanian dinar became the kingdom’s official currency, and use of the Palestinian pound ceased in the kingdom on 30 September 1950. Although issued by the Jordan Currency Board, the notes bear the name of The Hashemite Kingdom of the Jordan.
Until 1992, coins were denominated in Arabic using fils, qirsh, dirham and dinar but in English only in fils and dinar. Since 1992, the fils and dirham are no longer used in the Arabic denominations and the English denominations are given in dinar and either qirsh or piastres.
My Collection of Jordanian Coins. I have only one coin of Jordan in the Album, as on today.
25 Fils - Jordan - Cupro Nickel - 1977
Note - Some of the images of coins in my collection, have been taken from the Gallery to the extent available, to save on time & effort involved in photography & editing.































